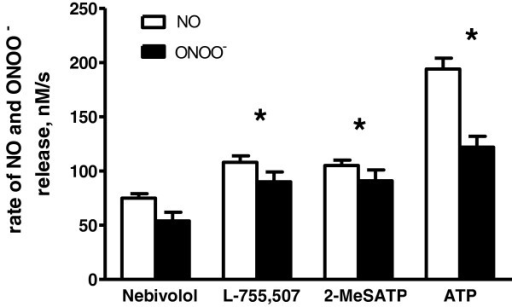
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling
Protease-activated receptors (PARs) and the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. In this review, we focus on the regulatory mechanism of ectodomain shedding by ADAM10/17 metalloprotease via GPCR signaling. PAR2 and NK1R induce membrane blebbing, resulting in phosphatidylserine externalization in the cellular membrane, which is required for ADAM10/17 metalloprotease activation.
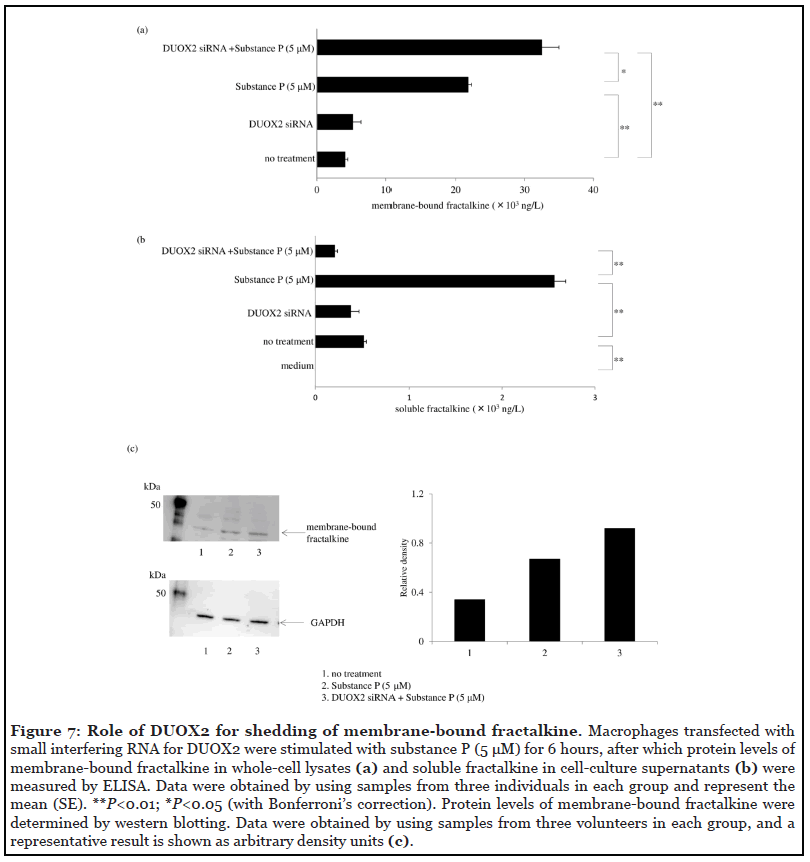
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling
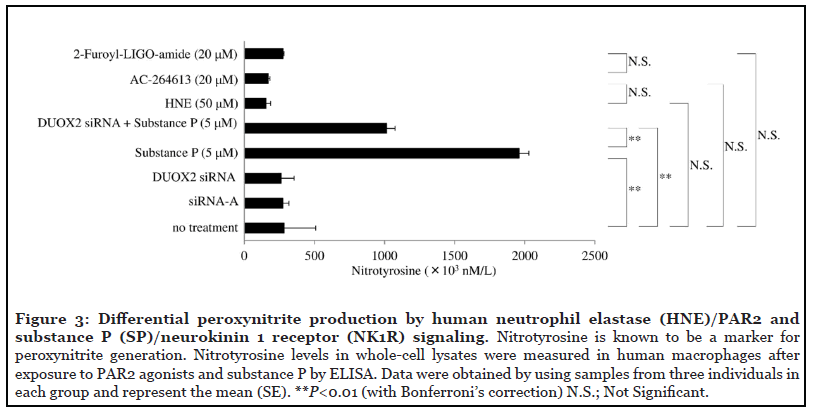
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling

ADAM17 mediates cardiovascular diseases via ectodomain shedding. A

Proteolytic ectodomain shedding of membrane proteins in mammals—hardware, concepts, and recent developments
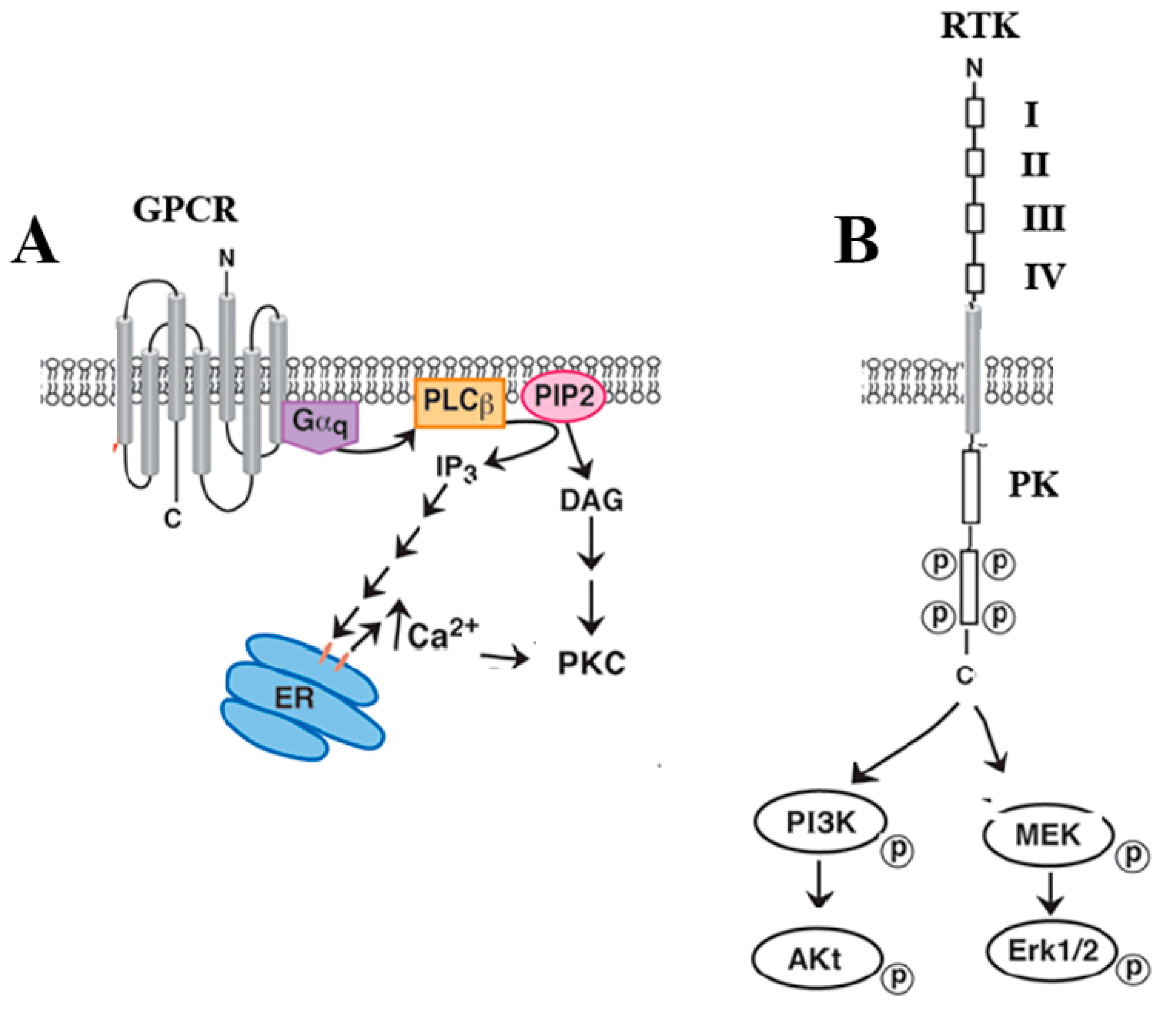
Biology, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text

The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling

Exploring the landscape of ectodomain shedding by quantitative protein terminomics - ScienceDirect

Biology, Free Full-Text
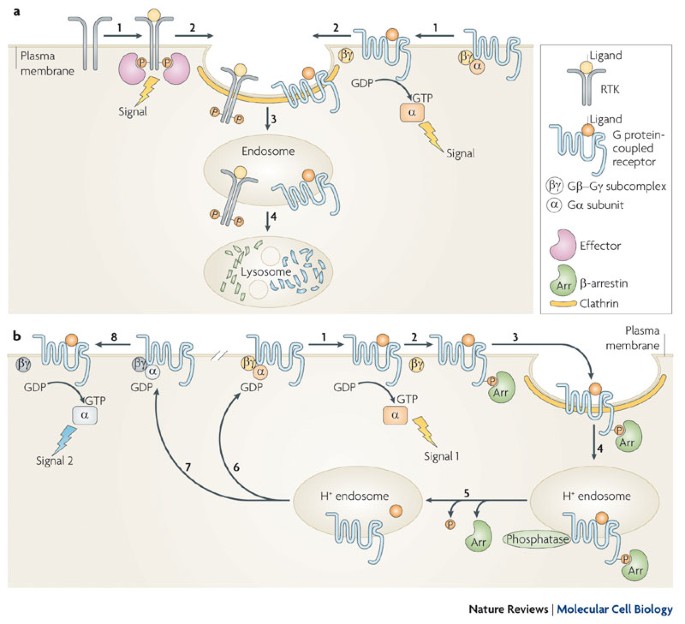
Endocytosis and signalling: intertwining molecular networks
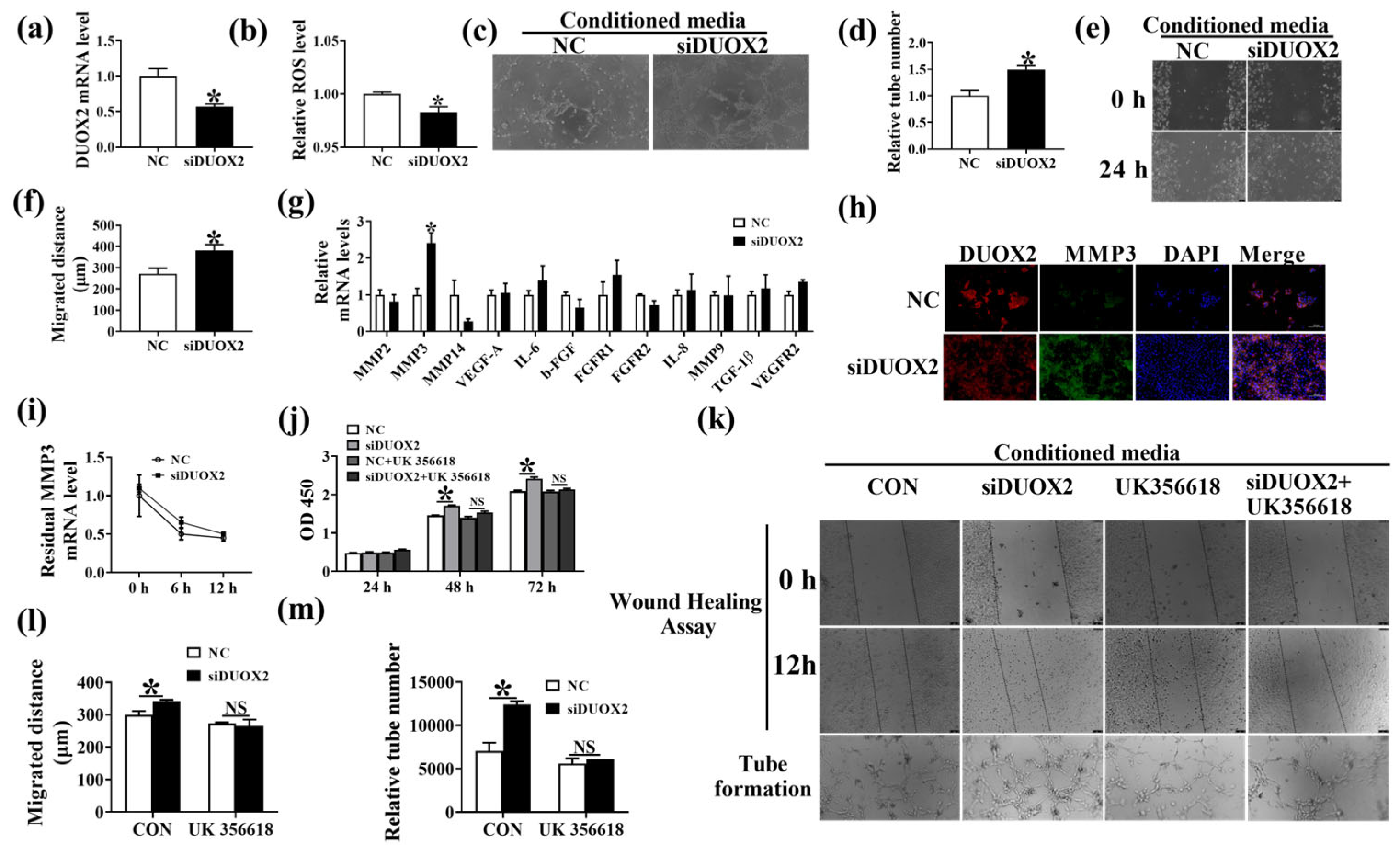
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

SALSA, a genetically encoded biosensor for spatiotemporal quantification of Notch signal transduction in vivo. - Abstract - Europe PMC
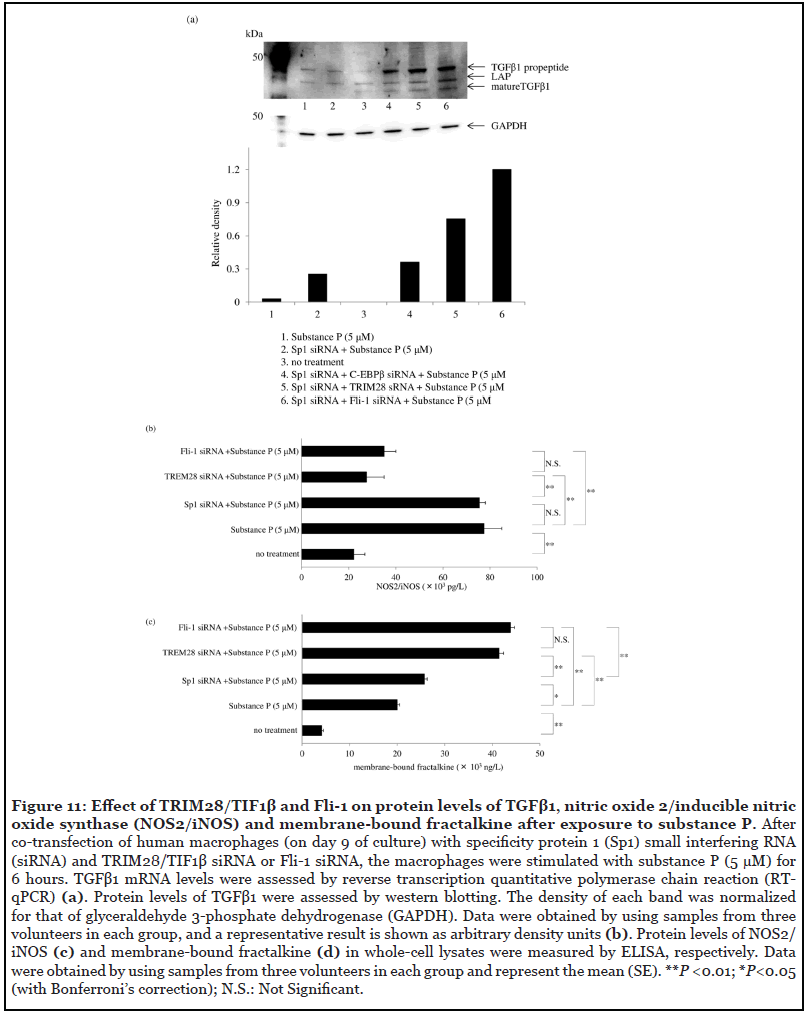
The Role of Membrane-embedded DUOX2 on Ectodomain Shedding via G protein-coupled Receptor Signaling

Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology